The journey to becoming a parent is one of life’s most exciting and life-changing adventures. It’s a time filled with hope, anticipation, and sometimes a few unanswered questions. Understanding how to get pregnant is key for anyone hoping to welcome a new family member. While it may seem simple, several necessary steps and details can significantly enhance your chances of success. From knowing your body’s signals to making healthy choices, every piece of the puzzle plays a big part in helping you conceive.
Often, people have misconceptions about pregnancy that aren’t entirely accurate. These myths can cause confusion or worry. Our goal is to provide you with clear and accurate information to support you on your path to getting pregnant. By understanding the real facts, you can feel more confident and prepared for this amazing journey.
Key Takeaways
- Understand Your Cycle: Knowing your menstrual cycle and pinpointing ovulation is crucial for timing intercourse effectively.
- Prioritize Health: A healthy lifestyle for both partners, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and effective stress management, significantly enhances fertility.
- Seek Early Guidance: Consulting a healthcare professional before trying to conceive is a smart first step to ensure you’re both physically and emotionally ready.
- Be Patient & Positive: Getting pregnant can take time. Stay hopeful, manage stress effectively, and support one another throughout the process.
- Know When to Get Help: If conception takes longer than expected, don’t hesitate to seek advice from fertility specialists.
Understanding the Menstrual Cycle: Your Body’s Rhythm
Your menstrual cycle is like a monthly show your body puts on to get ready for a possible pregnancy. Knowing its different acts is super helpful when you’re trying to figure out how to get pregnant.
Explanation of the Menstrual Cycle Phases
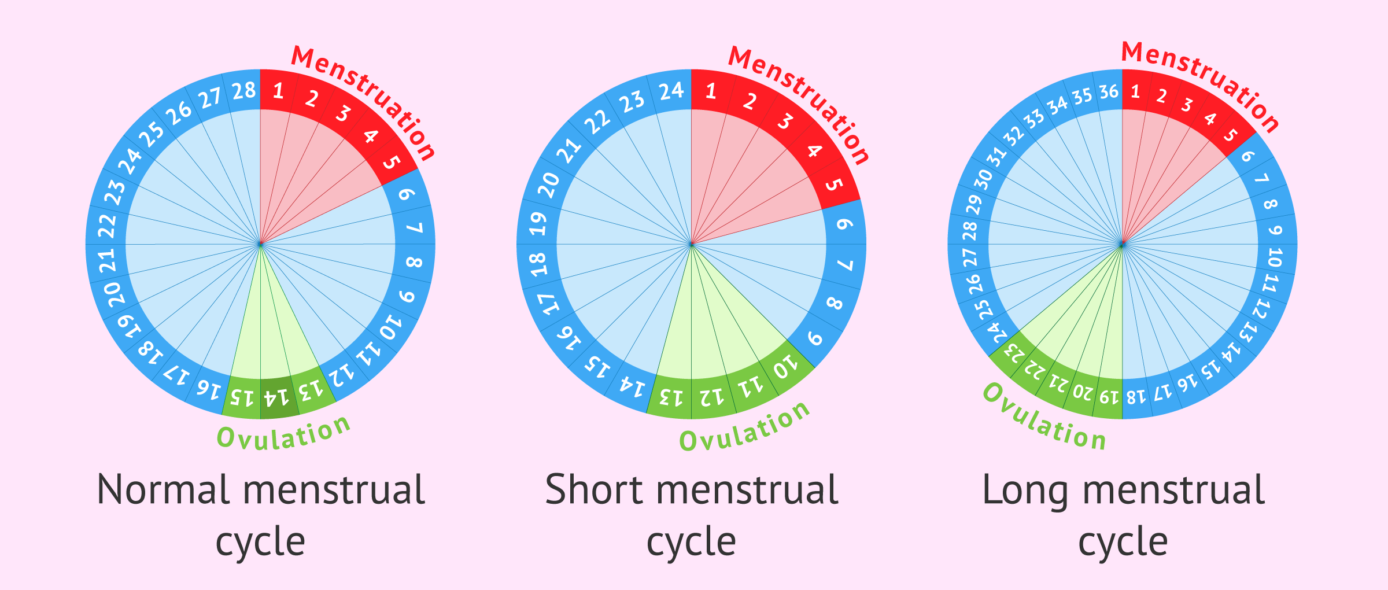
The cycle typically lasts about 21 to 35 days and has four main parts, each with special jobs:
- Menstrual Phase (Days 1-5, roughly): 🩸 This is when you have your period. If you didn’t get pregnant in the last cycle, your body sheds the lining of your uterus. It’s the start of a new cycle!
- Follicular Phase (Days 1-14, roughly): 🥚 After your period, your body starts getting ready for ovulation. Hormones like Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) tell your ovaries to grow tiny sacs called follicles. Each follicle holds an egg. One egg usually grows larger and prepares to be released. Your uterine lining also starts to thicken again, preparing a cozy home for a fertilized egg.
- Ovulatory Phase (Around Day 14 for a 28-day cycle): 🎯 This is the main event! Luteinizing Hormone (LH) surges, telling the biggest follicle to burst open and release its mature egg. This is called ovulation. The egg then travels down the fallopian tube, waiting for sperm. An egg can only be fertilized for about 12 to 24 hours after it’s released. This is your most fertile time!
- Luteal Phase (Days 15-28, roughly): ✨ After ovulation, the empty follicle changes into something called the corpus luteum. This little helper makes progesterone, a hormone that keeps the uterine lining thick and ready for a fertilized egg. If the egg is fertilized and implants, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone to support the early pregnancy. If no pregnancy happens, the corpus luteum breaks down, progesterone levels drop, and your period starts again.
“Understanding these phases empowers you to make informed decisions about the best times to engage in sexual activity for successful conception.”
The Importance of Tracking Ovulation
Since the egg only lives for a short time after release, knowing exactly when you ovulate is super important for getting pregnant. This helps you pinpoint your “fertile window” – the best days to have sex to increase your chances.
Here are some popular ways to track ovulation:
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT): Your BBT is your lowest body temperature when you’re fully at rest. Right after ovulation, your BBT usually goes up by a small amount (about 0.5 to 1 degree Fahrenheit) and stays higher until your next period. By tracking it every morning before you get out of bed, you can observe this shift and confirm that ovulation has occurred.
- Cervical Mucus (CM): Your cervical mucus changes throughout your cycle. Before ovulation, it often becomes clear, slippery, and stretchy, like raw egg whites. This “fertile” mucus helps sperm travel and survive. After ovulation, it usually becomes thicker or disappears.
- Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): These are like home pregnancy tests, but they detect the LH surge that happens just before ovulation. You pee on a stick, and if you see a positive result, it means you’re likely to ovulate within the next 24-36 hours. This is a highly accurate and popular method for determining your fertile window.
- Fertility Tracking Apps: Many apps can help you log your BBT, CM, OPK results, and period dates. They use this information to predict your ovulation and fertile window. Just remember, these are predictions and should be used with other methods for the best results.
| Tracking Method | How It Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basal Body Temp | Confirms ovulation after it happens and requires consistency. | Affordable, helps confirm ovulation. | It can be subjective and requires practice to interpret. |
| Cervical Mucus | Observes changes in mucus consistency (egg-white like is fertile). | Free, gives real-time info. | Predictions can be off, as they are only as accurate as the data you input. |
| Ovulation Predictor Kits | Detects LH surge before ovulation. | Accurate, identifies fertile window in advance. | It can be more expensive, and it may not be effective for everyone (e.g., women with PCOS). |
| Fertility Apps | Uses data (LMP, cycle length, BBT, OPK) to predict fertile window. | Convenient, helps visualize patterns. | Predictions can be off, only as accurate as the data you input. |
By combining these methods, you can get a clearer picture of your body’s fertile window and increase your chances of getting pregnant.
Preparing for Pregnancy: Setting the Stage for Success
Before you even start trying to conceive, getting your body ready is a huge step in how to get pregnant successfully. Think of it as preparing your home for a new arrival!
Importance of a Healthy Lifestyle Before Conception
Your health before pregnancy lays the groundwork for a healthy pregnancy and baby. This is called preconception health.
- Balanced Diet: Eating well provides your body with all the nutrients needed for healthy eggs and sperm. We’ll dive deeper into this soon!
- Regular Exercise: Staying active helps manage weight, reduce stress, and improve overall health, all of which support fertility.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can impact your hormones and make conception more challenging. Finding ways to relax is key.
- Healthy Weight: Being underweight or overweight can mess with your hormones and make ovulation irregular. Aim for a healthy Body Mass Index (BMI).
- Avoid Harmful Substances: Things like smoking, excessive alcohol, and recreational drugs can seriously harm fertility for both partners and affect a developing baby. Quitting these before trying to conceive is vital.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional for Preconception Advice
This is a super smart move! Before you start trying to get pregnant, schedule a visit with your doctor, gynecologist, or reproductive specialist.
Here’s what they can help you with:
- Overall Health Check: They’ll review your medical history, including any chronic conditions (such as diabetes or thyroid issues), and the medications you’re taking. They can make sure everything is under control before pregnancy.
- Vaccinations: They’ll check your immunity to diseases like rubella (German measles) and chickenpox, which can be dangerous during pregnancy. You might need booster shots.
- Prenatal Vitamins: Your doctor will likely recommend starting a prenatal vitamin, especially one with folic acid, at least one month before you start trying. Folic acid is crucial for preventing severe birth defects of the brain and spine.
- Lifestyle Counseling: They can offer personalized advice on diet, exercise, and quitting any unhealthy habits.
- Genetic Counseling: If there’s a family history of certain genetic conditions, they might suggest genetic screening.
“Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals before attempting to conceive is a prudent step in the journey to becoming a parent.”
Nutrition and Diet: Fueling Your Fertility
What you eat plays a huge role in how to get pregnant, for both partners! Think of food as the fuel that keeps your reproductive system running smoothly.
Role of Balanced Nutrition in Fertility
Your body needs the right building blocks to make healthy eggs and sperm, and to create a welcoming environment for a baby.
- Vitamins and Minerals: These are like tiny workers that help your body do important jobs. For fertility, nutrients such as folate, iron, zinc, selenium, vitamin D, and vitamin B12 are vital.
- Antioxidants: These protect your cells, including egg and sperm cells, from damage. You find them in colorful fruits and veggies.
- Healthy Fats: Essential fatty acids, like omega-3s, are important for hormone production and cell health.
- Fiber: Helps regulate hormones and manage blood sugar.
Foods to Include for Optimal Reproductive Health
Focus on a rainbow of whole, unprocessed foods. Here are some fertility-boosting superstars:
- Folate-Rich Foods: Essential for preventing neural tube defects in early pregnancy.
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale) 🥬
- Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruit) 🍊
- Beans, lentils, chickpeas
- Avocado 🥑
- Iron-Rich Foods: Helps prevent anemia, which can affect fertility and pregnancy.
- Lean meats (beef, chicken) 🥩
- Beans, lentils
- Spinach
- Fortified cereals
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Good for hormone balance and egg/sperm quality.
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) 🐟
- Walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds
- Antioxidant Powerhouses: Protect reproductive cells.
- Berries (blueberries, raspberries) 🍓
- Nuts (almonds, pecans)
- Brightly colored vegetables (bell peppers, broccoli) 🥦
- Whole Grains: Provide fiber and stable energy.
- Oats, quinoa, brown rice, whole-wheat bread
- Lean Proteins: Important for egg and sperm development.
- Chicken, fish, beans, tofu, eggs 🥚
Try to limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive caffeine, as these can negatively impact your fertility.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: A Key to Getting Pregnant
Your body weight plays a big part in how to get pregnant, for both women and men. It’s all about balance!
Impact of Weight on Fertility
- For Women:
- Overweight/Obese: Too much body fat can disrupt hormone balance, especially estrogen, leading to irregular periods and problems with ovulation. It can also increase the risk of conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), which is a common cause of infertility.
- Underweight: Not having enough body fat can also mess with hormones, sometimes causing periods to stop altogether (amenorrhea), meaning no ovulation.
- For Men:
- Overweight/Obese: Can lead to lower testosterone levels, poorer sperm quality (lower count, slower movement, abnormal shape), and erectile dysfunction.
Tips for Achieving and Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Achieving a healthy weight isn’t just about looking good; it’s about optimizing your body for conception.
- Balanced Diet: Focus on nutrient-dense foods (as discussed above) and watch your portion sizes.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days of the week.
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to what you eat, when you eat, and why you eat. Avoid eating out of boredom or stress.
- Professional Support: Don’t be afraid to talk to a doctor, registered dietitian, or nutritionist. They can help you create a personalized plan that fits your needs and goals.
Importance of Regular Exercise: Moving Towards Parenthood
Staying active is another great way to improve your chances of getting pregnant. Exercise offers numerous benefits beyond just physical fitness.
Benefits of Exercise on Reproductive Health
- Hormone Regulation: Exercise helps maintain hormone balance, which is crucial for regular ovulation and healthy sperm production.
- Weight Management: As we just discussed, maintaining a healthy weight is vital for fertility. Exercise is a key part of this.
- Improved Blood Circulation: Adequate blood flow to your reproductive organs is crucial for their proper function.
- Stress Reduction: Exercise is a fantastic way to reduce stress. When you’re less stressed, your body is more likely to function optimally for conception.
- Better Sleep: Regular physical activity can lead to improved sleep, which in turn supports overall health and hormone balance.
Types of Exercise Suitable for Aspiring Parents
While exercise is beneficial, intense or extreme workouts can sometimes have a negative impact on fertility. The key is moderation and consistency.
- Low-Impact Aerobics:
- Walking 🚶♀️: Easy to start, can be done anywhere.
- Swimming 🏊♀️: Gentle on joints, great full-body workout.
- Cycling (stationary or outdoor) 🚴♀️
- Strength Training: Using light weights or your own body weight helps build muscle, which in turn boosts your metabolism.
- Flexibility and Mind-Body:
- Yoga 🧘♀️: Improves flexibility, reduces stress, and promotes relaxation.
- Pilates: Strengthens core muscles and improves posture.
Listen to your body, and if you’re unsure, always consult your doctor to determine the best exercise routine for you.
Managing Stress and Mental Health: A Calm Path to Conception
Trying to get pregnant can be a rollercoaster of emotions. Stress and mental well-being are deeply connected to your fertility journey.
Effects of Stress on Fertility
When you’re stressed, your body produces stress hormones, such as cortisol. These hormones can:
- Disrupt Ovulation: High stress can interfere with the hormones that regulate ovulation, causing irregular cycles or even stopping ovulation altogether.
- Affects Sperm Quality: For men, chronic stress can negatively impact sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Reduce Libido: Stress can make you less interested in sex, which naturally reduces opportunities for conception.
- Impact Overall Health: Long-term stress can weaken your immune system and lead to other health problems that might indirectly affect fertility.
Techniques for Reducing Stress and Promoting Emotional Well-being
Taking care of your mind is just as important as taking care of your body.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Even a few minutes a day can help calm your mind. There are many apps and guided meditations available.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Simple techniques can quickly lower your heart rate and promote relaxation.
- Engage in Hobbies: Do things you love! Reading, painting, gardening, playing music – anything that brings you joy and takes your mind off trying to conceive.
- Regular Exercise: As mentioned, it’s a fantastic stress reliever.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Connect with Loved Ones: Discuss your feelings openly with your partner, friends, or family. Sharing your journey can lighten the load.
- Professional Support: Don’t hesitate to seek help from a therapist or counselor. They can provide coping strategies and emotional support, especially if you’re struggling with anxiety or depression related to fertility. Support groups can also be beneficial for connecting with others who understand what you’re going through.
“The intricate connection between stress and fertility is well-documented. High levels of stress can disrupt hormonal balance, ovulation, and overall reproductive function.”
Timing Intercourse: Maximizing Your Chances
Once you understand your cycle and ovulation, the next big step in how to get pregnant is knowing when to have sex!
Best Times for Sexual Intercourse During the Menstrual Cycle
The key is to have sperm waiting for the egg when it’s released. Sperm can live inside the female reproductive tract for up to 5 days, while an egg only lives for 12-24 hours. This means your “fertile window” is typically the 5 days leading up to ovulation and the day of ovulation itself.
- Days Before Ovulation: Having sex in the 2-3 days before ovulation is often considered the most effective. This ensures there’s a fresh supply of healthy sperm ready and waiting when your egg is released.
- Day of Ovulation: Having sex on the day of ovulation is also highly effective.
- Regularity: While timing is important, having regular intercourse (2-3 times a week) throughout your cycle can also increase your chances, as it ensures you don’t miss any unexpected ovulation.
Maximizing Chances of Conception Through Timing
- Don’t Overdo It: Having sex every single day might actually reduce sperm quality in some men. Every other day or every two days during your fertile window is usually sufficient.
- Focus on the Fertile Window: Use your ovulation tracking methods (OPKs, CM, BBT) to identify your most fertile days.
- Keep it Fun: Don’t let the “timing” take all the joy out of intimacy. Remember, connecting with your partner is just as important!
Male Fertility Factors: Half the Equation for Getting Pregnant
While much of the focus is often on the female body, male fertility is equally important when trying to get pregnant. It takes two to tango!
Discussion of Male Fertility and Factors Affecting It
Male fertility largely depends on the quality and quantity of sperm. Key factors include:
- Sperm Count: How many sperm are in a given amount of semen? A low count means fewer chances for an egg to be fertilized.
- Sperm Motility: How well the sperm move. They need to be strong swimmers to reach the egg.
- Sperm Morphology: The shape and structure of the sperm. Sperm with abnormal shapes may have difficulty fertilizing an egg.
- Overall Health: Lifestyle habits, age, and underlying medical conditions can all affect male reproductive health.
Tips for Maintaining Optimal Male Reproductive Health
Men can take many proactive steps to boost their fertility:
- Healthy Diet: Just like women, men benefit from a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Antioxidants (found in berries, nuts, leafy greens) are especially good for sperm health.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity can affect hormone levels and sperm quality.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate exercise helps maintain overall health and can improve sperm parameters.
- Avoid Harmful Substances:
- Smoking: Damages sperm DNA and reduces count and motility.
- Excessive Alcohol: Can lower testosterone and affect sperm production.
- Recreational Drugs: Many can negatively impact sperm.
- Limit Heat Exposure: High temperatures can harm sperm production. Avoid hot tubs, saunas, and keeping laptops directly on your lap for long periods.
- Manage Stress: Stress can affect hormone levels and sperm quality.
- Regular Check-ups: Talk to your doctor about any concerns. They can check for underlying medical conditions like hormonal imbalances or infections that might affect fertility.
Female Fertility Factors: What Influences Your Chances
Understanding the factors that influence female fertility is crucial for any woman asking how to get pregnant.
Factors Influencing Female Fertility
- Age: This is one of the most significant factors. A woman’s egg quantity and quality naturally decline with age, particularly after the age of 35. This makes it harder to conceive and increases the risk of miscarriage.
- Hormonal Balance: Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, or issues with the pituitary gland can disrupt ovulation.
- Ovulation Disorders: Irregular or absent ovulation is a common cause of female infertility.
- Structural Issues:
- Blocked Fallopian Tubes: Can prevent the egg from meeting sperm or a fertilized egg from reaching the uterus. Often caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or endometriosis.
- Uterine Problems: Fibroids (non-cancerous growths), polyps, or an abnormally shaped uterus can interfere with implantation.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, potentially causing inflammation and scarring that affects fertility.
- Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI): When the ovaries stop functioning normally before age 40.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol, recreational drug use, extreme weight (underweight or overweight), and high stress can all negatively impact fertility.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Untreated STIs like chlamydia or gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and lead to blocked fallopian tubes.
Strategies for Promoting Female Reproductive Wellness
- Regular Gynecological Check-ups: Essential for early detection and management of any issues.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: Collaborate with your doctor to effectively control conditions such as PCOS, diabetes, or thyroid issues.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy weight, eat a balanced diet, exercise moderately, and manage stress.
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol: These are critical steps for improving egg quality and overall reproductive health.
- Practice Safe Sex: Prevent STIs that can harm fertility.
- Consider Fertility Preservation: If you’re young and not ready for children but concerned about age-related decline, discuss options like egg freezing with a specialist.
Healthy Habits for Both Partners: A Shared Journey
Getting pregnant is a team effort! When both partners commit to a healthy lifestyle, it strengthens their chances and their relationship.
Importance of Mutual Commitment to a Healthy Lifestyle
- Shared Goals: When you’re both working towards a common goal (a healthy baby!), It’s easier to stay motivated.
- Mutual Support: You can encourage each other by cooking nutritious meals together, going for walks, or finding ways to relax.
- Stronger Bond: Navigating this journey together, especially with its ups and downs, can truly strengthen your relationship.
Benefits of Supporting Each Other’s Fertility Goals
- Increased Chances: When both egg and sperm are at their healthiest, the chances of conception naturally increase.
- Emotional Well-being: Knowing you’re not alone in this journey, and having a supportive partner, can significantly reduce stress and anxiety.
- Preparation for Parenthood: Learning to work as a team, communicate openly, and support each other through challenges sets a wonderful foundation for parenting.
Understanding Reproductive Health Issues: When Things Get Tricky
Sometimes, getting pregnant isn’t as straightforward as it seems. Various reproductive health issues can make conception challenging.
Common Fertility-Related Conditions and Their Impact
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A common hormonal disorder in women that can cause irregular or absent ovulation, making it difficult to predict fertile windows or ovulate at all.
- Endometriosis: As mentioned earlier, this condition can cause inflammation, scarring, and blockages that hinder conception.
- Fibroids: Non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can affect implantation or egg transport.
- Blocked Fallopian Tubes: Often due to infection (like from STIs) or previous surgeries, preventing egg and sperm from meeting.
- Male Factor Infertility: Issues with sperm production, movement, or shape.
- Unexplained Infertility: Sometimes, even after thorough testing, doctors can’t find a clear reason why a couple isn’t conceiving. This can be frustrating, but it doesn’t mean it’s impossible to get pregnant.
Seeking Medical Help for Unresolved Issues
If you’ve been trying to get pregnant for a while without success, it’s really important to seek medical advice.
- When to See a Specialist:
- If you’re under 35 and have been trying for 12 months or more without success.
- If you’re 35 or older and have been trying for 6 months or more without success.
- If you have known conditions that affect fertility (e.g., PCOS, endometriosis, irregular periods, history of STIs, male factor issues).
- What to Expect: A fertility specialist will conduct a thorough evaluation, which might include:
- Hormonal Blood Tests: For both partners.
- Semen Analysis: To check male fertility factors.
- Ovulation Tracking: More detailed monitoring.
- Ultrasound Scans: To check the ovaries and uterus.
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG): An X-ray to check if the fallopian tubes are open.
Early detection and treatment can significantly improve your chances of getting pregnant.
When to Seek Professional Help: Your Fertility Timeline
Knowing when to reach out for professional help is a critical part of the journey to getting pregnant.
Signs Indicating Potential Fertility Issues
Beyond the general guidelines (12 months of trying for under 35s, 6 months for over 35s), certain signs should prompt an earlier visit to a doctor or fertility specialist:
- Irregular or Absent Periods: This often signals ovulation problems.
- Very Painful Periods: Could indicate endometriosis or fibroids.
- History of Pelvic Infections or STIs: These can cause blocked fallopian tubes.
- Known Medical Conditions: Such as PCOS, thyroid disease, diabetes, or autoimmune disorders.
- Previous Surgeries: Especially on the ovaries, uterus, or testicles.
- Male Concerns: History of testicular injury, erectile dysfunction, or low libido.
- Age: If the female partner is 35 or older.
Overview of Fertility Tests and Treatments
Once you see a specialist, they’ll work to understand the root cause of any difficulties in getting pregnant.
- Diagnostic Tests: As mentioned above (hormone tests, semen analysis, ultrasounds, HSG).
- Treatment Options:
- Ovulation Induction: Medications (like Clomid or Letrozole) to stimulate ovulation.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Specially prepared sperm are placed directly into the uterus around the time of ovulation.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Eggs are retrieved from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a lab. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the uterus. This is a more complex but often highly effective treatment.
- Donor Eggs/Sperm/Embryos: If there are severe issues with one partner’s gametes.
- Surgery: To correct issues like fibroids, endometriosis, or blocked tubes.
Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, not failure. Many couples successfully get pregnant with the help of fertility treatments.
Medical Interventions and Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): Advanced Paths to Parenthood
For some couples, natural conception or basic treatments aren’t enough. That’s where advanced medical interventions, known as Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART), come in to help them get pregnant.
In-depth Explanation of Fertility Treatments (IVF, IUI, etc.)
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI):
- Process: Often used for mild male factor infertility, unexplained infertility, or issues with cervical mucus. Sperm are “washed” (separated from seminal fluid) and concentrated. They are then placed directly into the woman’s uterus using a thin catheter around the time of ovulation.
- Success Rates: Vary widely depending on age and diagnosis, but generally lower than IVF.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF):
- Process: This is the most common and effective ART.
- Ovarian Stimulation: Medications are given to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
- Egg Retrieval: Eggs are collected from the ovaries using a needle guided by ultrasound.
- Fertilization: Eggs are combined with sperm in a lab dish. Sometimes, a single sperm is injected directly into an egg (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection or ICSI) for male factor infertility.
- Embryo Culture: Fertilized eggs (embryos) are grown in the lab for a few days.
- Embryo Transfer: One or more healthy embryos are transferred into the woman’s uterus.
- Success Rates: Higher than IUI, but still vary greatly by age, cause of infertility, and clinic.
- Process: This is the most common and effective ART.
- Other ARTs:
- Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT) / Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT): Less common now, these involve transferring eggs and sperm (GIFT) or fertilized eggs (ZIFT) directly into the fallopian tube.
- Donor Eggs/Sperm/Embryos: Used when there are significant issues with a partner’s gametes or if a single parent is pursuing pregnancy.
Considerations When Exploring Assisted Reproduction Options
Choosing ART is a big decision with many factors to weigh:
- Success Rates: Understand the realistic chances for your specific situation.
- Financial Implications: ART can be very expensive, and insurance coverage varies.
- Emotional Toll: The process can be physically and emotionally demanding, with cycles of hope and disappointment. Support systems are crucial.
- Physical Side Effects: Medications can cause bloating, mood swings, and other side effects.
- Ethical Concerns: Issues like embryo disposition, multiple pregnancies, and genetic screening can raise ethical questions.
- Time Commitment: ART cycles require frequent clinic visits for monitoring.
It’s vital to have open conversations with your partner, fertility specialists, and potentially a counselor to make the best decision for your family.
Age and Fertility: The Biological Clock
Age is a significant factor in how to get pregnant, especially for women.
How Age Affects Fertility for Both Men and Women
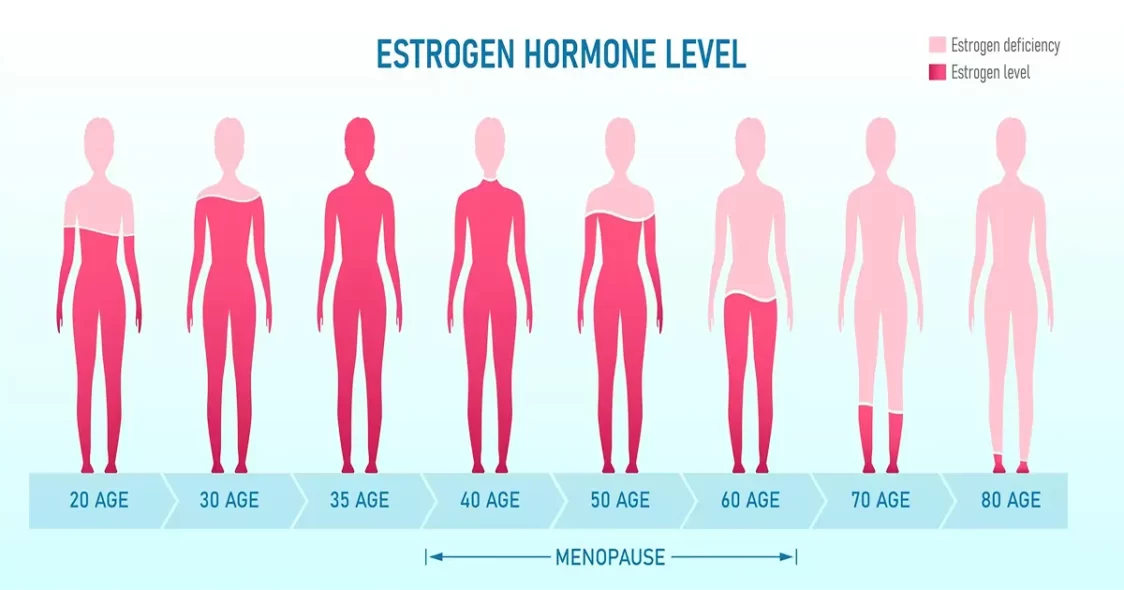
- Female Fertility:
- Quantity: Women are born with all the eggs they’ll ever have. As you age, the number of eggs naturally declines.
- Quality: The quality of eggs also decreases with age. Older eggs are more likely to have chromosomal abnormalities, which can lead to difficulty conceiving, miscarriage, or genetic conditions in the baby.
- Decline: Female fertility generally starts to decline in the early 30s, drops more significantly after 35, and accelerates after 40.
- Male Fertility:
- While men continue to produce sperm throughout their lives, sperm quality can also decline with age, typically after 40 or 50. This can include reduced sperm count, motility, and increased DNA fragmentation, potentially affecting the ability to get pregnant and increasing certain risks for the baby.
Family Planning Considerations Based on Age
- Earlier Conception: If you envision a large family, starting earlier can be beneficial due to the natural decline in female fertility.
- Fertility Preservation: For women who want to delay childbearing, egg freezing (oocyte cryopreservation) is an option to preserve younger, healthier eggs for future use.
- Open Discussion: Couples should openly discuss their family planning timeline, considering both partners’ ages and career goals.
- Consult a Specialist: If you’re approaching or over 35 and planning to conceive, or if you’ve been trying for 6 months without success, a fertility specialist can provide personalized advice and discuss options.
Overcoming Infertility Challenges: A Journey of Resilience
The path to getting pregnant isn’t always smooth. Facing infertility can be one of the most challenging experiences for a couple.
Coping with the Emotional Aspects of Infertility
It’s completely normal to feel a wide range of emotions when dealing with infertility:
- Sadness and Grief: For the loss of the dream of a natural conception.
- Frustration and Anger: At your body, the situation, or even others who conceive easily.
- Stress and Anxiety: About treatments, finances, and the unknown future.
- Guilt and Blame: Feeling like it’s your fault or blaming your partner.
- Isolation: Feeling like no one truly understands what you’re going through.
It’s vital to acknowledge these feelings and allow yourself to feel them. Don’t bottle them up.
Support Networks and Resources for Individuals and Couples
You don’t have to go through this alone. Building a strong support system is crucial:
- Partner Communication: Talk openly and honestly with your partner. Share your feelings, fears, and hopes. Support each other.
- Friends and Family: Choose a few trusted people you can confide in. Be clear about what kind of support you need (e.g., listening, distraction, not unsolicited advice).
- Therapy/Counseling: A therapist specializing in fertility can provide coping strategies, help you process emotions, and improve communication with your partner.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who understand your journey can be incredibly validating. Online forums and local groups offer a safe space to share experiences and advice. Organizations like RESOLVE: The National Infertility Association offer resources.
- Self-Care: Prioritize activities that help you relax and recharge, whether it’s exercise, hobbies, or quiet time.
Remember, infertility is a medical condition, and seeking help is a brave step. You are resilient, and there are many paths to building a family.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Fertility: What to Avoid
Certain lifestyle choices can significantly impact your ability to get pregnant for both partners.
Impact of Smoking, Alcohol, and Substance Use on Fertility
- Smoking (Cigarettes, Vaping, Marijuana):
- Women: Damages eggs, reduces ovarian reserve, causes earlier menopause, increases risk of miscarriage, and ectopic pregnancy.
- Men: Reduces sperm count, motility, and morphology; damages sperm DNA.
- Alcohol:
- Women: Heavy drinking can disrupt ovulation and increase the time it takes to conceive. No safe amount is known during pregnancy, so it’s often advised to stop when trying.
- Men: Excessive alcohol can lower testosterone, impair sperm production, and cause erectile dysfunction.
- Recreational Drugs (e.g., Cocaine, Opioids, Steroids): Can severely impact hormone production and sperm/egg quality, leading to infertility. Many are dangerous during pregnancy.
- Excessive Caffeine: While moderate caffeine intake (up to 200mg/day, about one 12oz cup of coffee) is generally considered safe, very high levels might be linked to reduced fertility and increased miscarriage risk.
Strategies for Quitting Harmful Habits
Quitting these habits can be tough, but it’s one of the best things you can do to improve your chances of getting pregnant and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
- Talk to Your Doctor: They can provide resources, support, and sometimes medication to help you quit.
- Set a Quit Date: Make a firm decision and stick to it.
- Seek Support: Tell your partner, friends, and family about your goal. Join support groups.
- Identify Triggers: Understand what makes you want to use the substance and find healthier coping mechanisms.
- Replace Habits: Find new, positive activities to fill the void left by the old habit (e.g., exercise, a new hobby).
“Overcoming addictive behaviors requires commitment and support. Seeking professional help, setting achievable goals, and involving partners in the process can increase the likelihood of successfully quitting harmful habits and improving fertility prospects.”
Environmental Factors and Fertility: What’s Around You
It’s not just what you put into your body; what’s around you can also affect your ability to get pregnant.
Discussion of Environmental Toxins and Their Effect on Fertility
Our modern world exposes us to many chemicals that can act as “endocrine disruptors.” This means they can interfere with your body’s hormone system, which is vital for reproduction.
- Pesticides and Herbicides: Found in conventionally grown produce. It can affect hormone balance and sperm quality.
- Phthalates and BPA (Bisphenol A): Common in plastics, food packaging, and personal care products. It can mimic hormones and disrupt reproductive function.
- Heavy Metals: Lead, mercury, and cadmium can be found in contaminated water, certain fish, or industrial pollution. It can negatively impact the quality of eggs and sperm.
- Air Pollution: Exposure to fine particulate matter can be linked to reduced fertility.
Minimizing Exposure to Potential Reproductive Disruptors
While you can’t avoid all toxins, you can take steps to reduce your exposure:
- Choose Organic: Opt for organic fruits and vegetables when possible, especially for foods on the “Dirty Dozen” list (foods with higher pesticide residues).
- Filter Your Water: Use a good-quality water filter to remove contaminants.
- Reduce Plastic Use:
- Store food in glass or stainless steel containers instead of plastic.
- Avoid heating food in plastic, especially in the microwave.
- Look for “BPA-free” and “phthalate-free” on products.
- Ventilate Your Home: Improve air quality by opening windows, using air purifiers, and avoiding strong chemical cleaners.
- Be Mindful of Personal Care Products: Many cosmetics and lotions contain phthalates or parabens. Look for “clean” or “natural” alternatives.
- Eat Lower-Mercury Fish: Choose fish like salmon, cod, and canned light tuna, and limit high-mercury fish like swordfish, shark, and king mackerel.
Importance of Prenatal Care: A Healthy Start
Once you successfully get pregnant, the next crucial step is starting prenatal care!
Initiating Prenatal Care Upon Confirmation of Pregnancy
As soon as you get a positive pregnancy test, contact your doctor or midwife to schedule your first prenatal appointment. This usually happens between 8 and 10 weeks of pregnancy. Early care is essential!
Benefits of Early Healthcare for the Mother and the Developing Baby
- Monitoring Health: Regular check-ups allow your healthcare provider to monitor your health and the baby’s growth and development.
- Early Detection of Issues: Identifying potential complications, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, or certain infections, enables timely treatment.
- Nutritional Guidance: You’ll receive advice on specific dietary needs during pregnancy, including continuing prenatal vitamins (mainly folic acid).
- Screening and Tests: Throughout your pregnancy, you’ll undergo various screenings and tests to ensure the health and development of your baby.
- Education and Support: Your appointments provide an excellent opportunity to ask questions, learn about what to expect, and receive support for any concerns you may have.
- Healthy Habits: Reinforces the importance of healthy eating, exercise, and avoiding harmful substances throughout pregnancy.
Early prenatal care sets the stage for a healthy pregnancy and a positive outcome for both mother and baby. You can learn more about common concerns during early pregnancy, like low belly pain in the first trimester of pregnancy or even very early signs of pregnancy at 1 week.
Healthy Pregnancy Habits: Nurturing Growth
Now that you’re getting pregnant, it’s time to adjust your daily routine to support your growing baby!
Nutritional Needs During Pregnancy
Your body requires additional nutrients to support the remarkable growth occurring within you.
- Folic Acid: Continue taking your prenatal vitamin with folic acid throughout pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects.
- Iron: Crucial for making red blood cells for you and your baby, preventing anemia. Found in lean meat, beans, and leafy greens.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Essential for the baby’s bones and teeth. Found in dairy, fortified plant milks, and leafy greens.
- Protein: For the baby’s growth and development. Found in lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Important for a baby’s brain and eye development. Found in fatty fish (low mercury) and flaxseeds.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water!
Aim for a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid raw fish, unpasteurized dairy products, and certain types of cheese.
Exercise, Rest, and Self-Care Recommendations for Expectant Mothers
Staying active and taking care of yourself are key to a healthy pregnancy.
- Exercise: If you were active before pregnancy, you can usually continue most activities, with modifications. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days. Good choices include walking, swimming, prenatal yoga, and dancing. Always consult your doctor about safe exercise during pregnancy.
- Rest: Your body is working hard! Listen to it and get plenty of rest. Naps are your friend!
- Self-Care: This is not a luxury, it’s a necessity!
- Manage Stress: Continue practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or gentle stretching.
- Prioritize Sleep: Create a comfortable sleep environment.
- Stay Hydrated: Carry a water bottle with you.
- Connect with Others: Talk to your partner, friends, or other expectant moms.
- Do What Makes You Happy: Read a book, take a warm bath (not hot!), listen to music.
Taking care of yourself helps you feel better and supports your baby’s development.
Understanding Conception Myths: Debunking Falsehoods

The world of getting pregnant is full of old wives’ tales and myths. Let’s set the record straight!
Debunking Common Misconceptions About Getting Pregnant
- Myth 1: Certain Sex Positions Guarantee Pregnancy (or a Boy/Girl).
- Truth: The position you have sex in has absolutely no impact on whether you get pregnant or the baby’s gender. Sperm are strong swimmers! What matters is that sperm reach the egg.
- Myth 2: You Must Lie Down with Your Legs Up After Sex.
- Truth: While it doesn’t hurt, there’s no scientific evidence that lying down with your legs elevated after sex increases your chances of getting pregnant. Sperm are already on their way!
- Myth 3: You Can Get Pregnant Only on Day 14 of Your Cycle.
- Truth: While Day 14 is a common average for ovulation in a 28-day cycle, cycles vary. Your fertile window is typically 5-6 days long, including the days leading up to ovulation and the day of ovulation. Rely on tracking methods, not just a calendar number.
- Myth 4: Stress Makes It Impossible to Get Pregnant.
- Truth: While high stress can definitely affect your cycle and make it harder to conceive, it doesn’t make it impossible. Many stressed people get pregnant. Managing stress is helpful, but don’t blame yourself if you’re stressed.
- Myth 5: Infertility is Always a Woman’s Problem.
- Truth: Infertility affects men and women equally. Male factor infertility accounts for about 30-40% of cases, and combined factors or unexplained infertility make up the rest.
Relying on Accurate Information and Science
When you’re trying to get pregnant, it’s easy to get overwhelmed by conflicting advice. Always choose reliable sources:
- Healthcare Professionals: Your doctor, gynecologist, or fertility specialist.
- Reputable Medical Websites: Look for sites ending in .org, .gov, or from well-known medical institutions.
- Evidence-Based Research: Information backed by scientific studies.
Don’t let myths add unnecessary worry to your journey. Focus on facts and take care of yourself!
Supporting a Positive Conception Mindset: Hope and Patience
The journey to getting pregnant can be emotionally demanding. Keeping a positive mindset is about managing your emotions, not ignoring them.
It’s natural to feel anxious when trying to conceive, especially if it takes longer than expected.
- Acknowledge Your Feelings: It’s okay to feel sad, frustrated, or stressed. Don’t judge yourself for these emotions.
- Practice Self-Compassion: Be kind to yourself. This journey is challenging, and you’re doing your best.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation: Utilize techniques such as deep breathing, meditation apps, or gentle yoga to calm your mind.
- Journaling: Writing down your thoughts and feelings can be a powerful way to process them.
- Limit “Fertility Talk” Time: Designate specific times to discuss fertility with your partner or support system, and then focus on other things.
- Seek Professional Help: If anxiety or depression becomes overwhelming, a therapist can provide valuable tools and support.
Fostering a Hopeful and Patient Attitude During the Journey
Addressing Anxiety and Stress Related to Conception
- Remember It Takes Time: For healthy couples, it can take several months or even up to a year to get pregnant. Try not to expect it to happen on the first try.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Did you track your ovulation perfectly? Did you and your partner have a lovely, intimate evening? Acknowledge these moments.
- Focus on the Present: While you have a future goal, try to appreciate your life as it is now. Don’t put everything on hold for pregnancy.
- Stay Informed, Not Obsessed: Learn what you need to know, but avoid constantly searching for new symptoms or comparing your journey to others.
- Trust the Process (and Your Doctors): Have faith that you are doing everything you can, and if medical help is needed, you are in good hands.
“Cultivating a hopeful and patient attitude is essential. Recognizing that the journey to conception may involve challenges and uncertainties allows couples to approach setbacks with resilience and maintain a sense of optimism throughout the process.”
Communication Between Partners: Building a Strong Foundation
Open and honest communication is the bedrock of a strong relationship, especially when you’re trying to get pregnant.
Importance of Open and Supportive Communication
- Shared Understanding: Talk about your hopes, fears, and expectations. What does getting pregnant mean to each of you?
- Emotional Support: This journey can be challenging. Be each other’s biggest cheerleaders and shoulders to cry on.
- Decision-Making: Discuss fertility treatments, financial implications, and lifestyle changes together. Make decisions as a team.
- Preventing Resentment: If one partner feels more burdened or isolated, resentment can build. Open communication helps prevent this.
Navigating Challenges as a Team and Strengthening the Relationship
- Active Listening: Truly hear what your partner is saying, without interrupting or judging.
- Empathy: Try to understand your partner’s perspective, even if it’s different from yours.
- “I” Statements: Express your feelings using “I” statements (“I feel sad when…”) instead of “you” statements (“You always make me feel…”).
- Set Aside Time: Schedule regular “check-ins” to talk about how you’re both feeling about the fertility journey.
- Seek Couple’s Counseling: If communication becomes strained or you’re struggling to cope, a therapist can provide tools and a safe space for open discussion.
When you face the challenges of getting pregnant as a united front, you not only increase your chances of success but also strengthen the very foundation of your future family.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Navigating Complexities
As you explore different paths to getting pregnant, especially with assisted reproductive technologies, legal and ethical questions can arise.
Discussing Legal and Ethical Aspects of Assisted Reproductive Technologies
- Parental Rights: Who are the legal parents if donor eggs, sperm, or surrogacy are involved? Laws vary by state and country.
- Donor Anonymity vs. Openness: Will you choose an anonymous donor or one who is open to contact later?
- Embryo Disposition: What happens to unused embryos from IVF? Options include donation to research, donation to other couples, or discarding them.
- Surrogacy Laws: Legal frameworks for surrogacy differ significantly. It’s crucial to have a clear contract and understand parental rights before starting.
- Genetic Screening: Ethical debates exist around preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) and screening for certain traits.
Ensuring a Well-Informed and Responsible Approach
- Consult Legal Experts: If considering donor gametes or surrogacy, work with a lawyer specializing in reproductive law.
- Fertility Clinic Policies: Understand your clinic’s policies on embryo storage, donor selection, and other procedures.
- Ethical Counseling: Many clinics offer ethical counseling to help you explore complex decisions.
- Research and Education: Learn as much as you can about the legal and ethical landscape of your chosen path.
Making informed decisions ensures that your journey to getting pregnant is not only successful but also legally sound and ethically responsible.
Cultural and Social Influences: The Broader Picture
Beyond the medical and personal aspects, cultural and social influences can also shape your journey to getting pregnant.
Recognizing How Culture and Society Can Impact Fertility Decisions
- Family Pressure: In some cultures, there’s immense pressure to have children soon after marriage, or to have a certain number or gender of children. This can add stress to the conception process.
- Societal Expectations: The idea of what a “family” looks like can be narrow in some societies, leading to feelings of inadequacy or judgment if one faces infertility or chooses alternative paths.
- Stigma: Infertility can carry a social stigma in many cultures, making it difficult for couples to openly discuss their struggles or seek help.
- Religious Beliefs: Religious views can influence decisions about fertility treatments, adoption, or family size.
- Gender Roles: Traditional gender roles might place unequal pressure on women to conceive or on men to prove their virility.
Making Choices That Align with Personal Values and Beliefs
- Self-Reflection: Take time to understand your own values and beliefs about family, parenthood, and fertility.
- Open Dialogue: Discuss cultural expectations with your partner and decide together how much you want to conform or diverge from them.
- Education: Learn about infertility and its causes to help educate family members or friends who might hold misconceptions.
- Set Boundaries: It’s okay to set boundaries with well-meaning but intrusive family members regarding personal questions about getting pregnant.
- Seek Support: Find support systems that validate your choices and values, even if they differ from broader cultural norms.
Your journey to getting pregnant should ultimately reflect your personal values and what feels right for your family.
Alternative Paths to Parenthood: Expanding Your Definition of Family
Sometimes, despite all efforts, traditional conception may not be possible. Thankfully, there are many beautiful ways to build a family.
Exploring Adoption, Surrogacy, and Other Non-Traditional Routes
- Adoption:
- Domestic Adoption: Adopting a child born in your own country, either through public (foster care) or private agencies.
- International Adoption: Adopting a child from another country.
- Open vs. Closed Adoption: The level of contact with the birth family.
- Surrogacy: A woman (the surrogate) carries a pregnancy for another person or couple.
- Gestational Surrogacy: The surrogate carries an embryo created from the intended parents’ (or donors’) egg and sperm. The surrogate has no genetic link to the baby. This is the most common type.
- Traditional Surrogacy: The surrogate’s own egg is used, meaning she is genetically related to the baby. This is less common and raises more complex legal and emotional issues.
- Foster Care: Providing a temporary home for children in need, with the possibility of adoption if reunification with the biological family isn’t possible.
- Donor Options: Using donor sperm, donor eggs, or donor embryos in conjunction with IVF.
Embracing Diverse Ways of Building a Family
The definition of family is constantly evolving. Embracing these diverse paths requires:
- An Open Heart: Be open to different ways of becoming a parent and loving a child.
- Education: Thoroughly research each option, including legal, financial, and emotional aspects.
- Patience: These paths can also be long and complex.
- Support: Connect with others who have built families through these routes.
Whether through biological conception, adoption, or surrogacy, the love and connection you share create a meaningful and fulfilling family bond. You might even find articles on topics like co-sleeping with your baby or how to approach challenging situations like worst punishments kids received from their parents.
Financial Planning for Pregnancy: Budgeting for Your Baby
Beyond the emotional and physical preparation, understanding the financial aspects of getting pregnant and having a baby is essential.
- Fertility Treatment Costs: If you require medical interventions like IUI or IVF, these can be very expensive. Research insurance coverage, payment plans, and potential grants or loans.
- Prenatal Care: Doctor visits, tests, and ultrasounds throughout pregnancy.
- Delivery Costs: Hospital fees, doctor’s fees, anesthesia, and potential C-section costs can add up quickly.
- Baby Essentials: Consider diapers, formula (if not breastfeeding), clothing, car seats, cribs, strollers, and other necessary gear.
- Lost Income: Consider the potential loss of income if one partner takes parental leave.
- Childcare: If both parents plan to work, childcare costs can be a significant ongoing expense.
Start researching costs early, create a budget, and consider setting aside savings specifically for pregnancy and baby-related expenses.
Pregnancy Readiness Checklist: Are You Ready?
To help you organize your journey to getting pregnant and beyond, here’s a handy checklist:
- Health & Lifestyle:
- [ ] Schedule a preconception check-up with your doctor.
- [ ] Start taking a prenatal vitamin with folic acid.
- [ ] Adopt a healthy, balanced diet.
- [ ] Achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- [ ] Incorporate regular, moderate exercise.
- [ ] Quit smoking, vaping, and recreational drugs.
- [ ] Limit alcohol and caffeine intake.
- [ ] Reduce exposure to environmental toxins.
- [ ] Implement stress management techniques.
- [ ] Get adequate sleep.
- Understanding Your Cycle:
- [ ] Start tracking your menstrual cycle.
- [ ] Learn to recognize your fertile window (BBT, CM, OPKs).
- [ ] Understand the best times for intercourse.
- Partner Involvement:
- [ ] Both partners commit to healthy habits.
- [ ] Engage in open and honest communication.
- [ ] Discuss family planning goals together.
- Emotional & Mental Prep:
- [ ] Find healthy ways to cope with stress and anxiety.
- [ ] Build a strong support network.
- [ ] Educate yourself with accurate information.
- Financial & Practical:
- [ ] Research potential costs of conception and pregnancy.
- [ ] Begin saving for baby-related expenses.
- [ ] Consider legal and ethical aspects if using ART or alternative paths.
Fertile Window Calculator 🗓️
Use this tool to estimate your ovulation day and most fertile window to help you on your journey to **get pregnant**.
Conclusion
The journey of how to get pregnant is unique for every individual and couple. It’s a path filled with hope, learning, and often, a need for patience. By understanding your body, adopting healthy habits, communicating openly with your partner, and knowing when to seek professional help, you can significantly increase your chances of successful conception.
Remember to be kind to yourselves throughout this process. Whether your journey is straightforward or involves unexpected twists, the goal remains the same: to welcome a new life into your family. Embrace each step with knowledge and a positive mindset, and be aware that numerous resources and support systems are available to guide you. Here’s to your incredible journey to parenthood!
FAQs
How will I get pregnant quickly?
There’s no magic button to get pregnant instantly, but you can boost your chances! The quickest way to understand your menstrual cycle is to become familiar with it, especially when you ovulate. Using methods like ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) and tracking cervical mucus can help pinpoint your most fertile days. Having intercourse regularly during this “fertile window” (the 5 days before and the day of ovulation) gives you the best shot. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle (including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management) can also improve fertility for both partners.
How long should a woman keep sperm inside to get pregnant?
Sperm are very tiny and fast swimmers! Once ejaculated, they quickly move into the cervix and uterus. There’s no specific amount of time a woman needs to keep sperm inside for getting pregnant. Lying down for 10-15 minutes after intercourse is often suggested, but it’s not scientifically proven to increase chances. The most important thing is that healthy sperm get into the reproductive tract around the time of ovulation. Sperm can survive inside the woman’s body for up to 5 days, waiting for the egg.
How many tries to get a girl pregnant?
There’s no specific number of “tries” that guarantees pregnancy or the gender of a baby. For healthy couples under 35, it can take up to a year of regular, unprotected intercourse to get pregnant. About 85% of couples conceive within 12 months. If it takes longer or if you have specific concerns, it’s a good idea to consult a doctor. The gender of a baby is determined by the sperm (X for a girl, Y for a boy) at the moment of fertilization, and there’s no reliable way to influence it through “tries” or timing.


